This guide is to walk you through best practices for implementing the Firebolt® Metrics module to ensure that the data generated by platform API calls can be used to properly triage and verify the health of your app.
At a high level, implementing metrics involves:
Understanding the specific states (e.g.,
preloading,playback) and scenarios (e.g., “App launch”, “Media playing”) for when to report app metrics.Ensuring your app can properly listen and respond to events as a part of your metrics implementation.
Including the required metrics calls within your app’s code.
Before you begin
You should have previously set up your app to run locally with basic Lifecycle Management functionality.
Baseline API reference
This guide uses baseline Metrics API methods that are a part of the minimum required implementation for your app to work properly on our platform. If you are not familiar with these methods, review the Baseline Metrics APIs.
Understanding media states
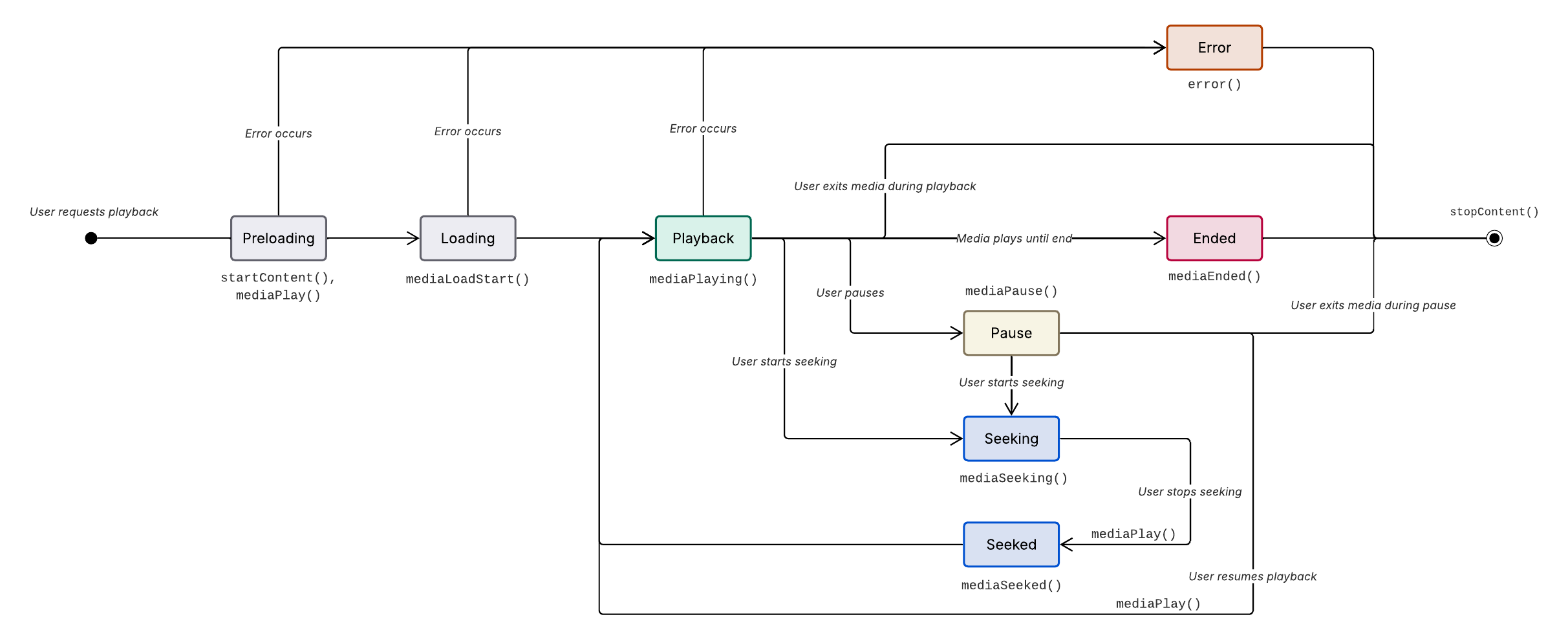
The metrics API calls in this guide are used to report specific events during associated states of media on the device. These media states are:
Preloading- The media has been requested by the user.Loading- The media is being requested from the CDN.Playback- The media is actively playing.Pause- The media has been paused.Seeking- The user has requested to jump forward or backward in the media.Seeked- The user has stopped jumping forward or backward in the media.Ended- The media has reached its conclusion after playback (including post-roll content if available).Error- The media has encountered an error with preloading, loading, or playback.
API calls are made at the start of each state
Metrics API calls sequences should be triggered at the start of their associated states (e.g.,
Metrics.mediaPlaying()is called at the start of thePlaybackstate).
App launch and media start metrics
App launch
Required Metrics API: Metrics.appInfo()
When an app launches from a cold start (i.e., was not active in any state, including background or suspend mode), it must call the Metrics.appInfo() API as early as possible. This API is essential for accurately recording events within the launched app build (i.e., version), ensuring consistency and reliability in event tracking and analysis.
To implement Metrics.appInfo(), include the call along with a specified build string in your app’s initialization function.
App launch sequence
App receives successful user request to launch from a cold start.
App calls
Metrics.appInfo()with specified build string.
// Package version that will be used as the appInfo build parameter value
const packageVersion = require('../package.json').version
// 1. App receives successful user request to launch from a cold start
async function init () {
// Call lifecycle.ready() to mark that it has launched.
try {
await Lifecycle.ready()
} catch (err) {}
// 2. App calls Metrics.appInfo() with specified build string (packageVersion).
await Metrics.appInfo(packageVersion)
// If desired, track what page is being displayed upon app start.
// In this case, the homepage is displayed. This may be replaced with a variable according to parameters.initialization() logic
Metrics.page('home')
video = document.getElementById('video')
// Register listeners for metrics media playback and interaction events
registerVideoEventListenersForMetrics(video)
/*
...Additional initialization logic...
*/
}Use Lifecycle.ready() to mark when your app has launched
The
Lifecycle.ready()method is called as early as possible in your app initialization. To learn more about Firebolt Lifecycle, check out our Lifecycle Management guide.
Media start
Required Metrics API: Metrics.startContent()
When your app receives a request from a user to start media playback (often via a Playback intent), it should call Metrics.startContent() to inform the platform that the user has started the primary content.
Media start sequence
App receives request from user to start playback of a media asset.
App calls
Metrics.startContent()to inform the platform that the user is engaged with the main content.App calls
Metrics.mediaPlay()to inform the platform that the user requested playback.
Gaming apps only require Metrics.appInfo() and Metrics.startContent()
If your app does not handle video playback (such as if it is a game), it does not need to call
Metrics.mediaPlay(). Additionally, it does not need to call any other media playback, interaction, or error metrics detailed in the rest of this guide.
// 1. App receives request from user to start playback of a media asset (represented here via Firebolt 'playback' intent).
if (intent.action == 'playback') {
const entityId = intent.data.entityId
// 2. App calls Metrics.startContent() to inform the platform that the user is engaged with the main content.
Metrics.StartContent(entityId)
// 3. App calls Metrics.mediaPlay() (as part of playById function) to inform the platform that the user requested playback.
playById(entityId)
}The Platform often uses Firebolt intents to communicate actions that your app must take in response to certain events. As such, the example above uses basic Firebolt intent logic to represent a user’s request to start the selected media.
Use Firebolt intents to flexibly manage interactions within your app
While your app must use Firebolt Intents to respond to platform events, it can also use intents to manage user interactions (e.g., playback, pause). Using intents to manage both Platform events and user interactions can improve performance and make your app easier to maintain.
Adding metrics listeners
Before delving into the main scenarios for media playback, we’ll want to review how to add metrics listeners. The code below shows a listener function that takes a video an argument and automatically reports all necessary metrics events for that video based on the specific metrics event. A call to the listener function can be included in the app initialization function (see code sample in App launch).
const PROGRESS_EVENT_INTERVAL = 60 // seconds
/**
* Registers event listeners for the video element for purposes of reporting metrics
* This function listens for various video events such as playback state changes and errors.
* @param {*} video
*/
function registerVideoEventListenersForMetrics (video) {
// Log a metric once video is playing
video.addEventListener('playing', () => {
Metrics.mediaPlaying(currentlyLoaded.id)
})
// Log a metric once video is paused
video.addEventListener('pause', () => {
Metrics.mediaPause(currentlyLoaded.id)
})
// Log metrics for when seeking starts
video.addEventListener('seeking', () => {
Metrics.mediaSeeking(currentlyLoaded.id, progress())
})
// Log metrics for when seeking ends
video.addEventListener('seeked', () => {
Metrics.mediaSeeked(currentlyLoaded.id, progress())
})
// Once the video has ended, log a metric and hide the player controls
video.addEventListener('ended', () => {
Metrics.mediaEnded(currentlyLoaded.id)
// stop() function containing Metrics.stopContent() call
stop()
})
// Log an error metric if the video encounters an error
video.addEventListener('error', (e) => {
Metrics.error(Metrics.ErrorType.MEDIA, 'CONTENT-002', 'Error occurred during playback of ' + currentlyLoaded.id, true, { entityId: currentlyLoaded.id })
// stop() function containing Metrics.stopContent() call
stop()
})
// Log metrics for buffering events (should not be used in initial video start)
// Metrics.mediaWaiting() is only used for uninitentional interruptions
video.addEventListener('waiting', () => {
Metrics.mediaWaiting(currentlyLoaded.id)
})
}Buffering
The metrics event listener code above also includes a waiting listener that logs metrics for when media is buffering. However, the Metrics.mediaWaiting() call should only be triggered for unintended video playback interruptions.
Do not trigger a waiting call during media start and seeking
During the Media start scenario above and the Media seeking and seeked scenario below, no
Metrics.mediaWaiting()event should be triggered since buffering is expected at the start of the playback and while seeking content.
Media playback and interaction metrics
Media playing
Required Metrics APIs: Metrics.startContent(), Metrics.mediaPlay(), Metrics.mediaLoadStart(), Metrics.mediaPlaying()
Once media playback has started in your app, Metrics.mediaPlaying() is called to mark when playback first begins or resumes from a different state.
You may have noticed that the code in the Media start scenario above uses a custom playById function. This function acts as a bundle of code needed to play associated media as well as handle our media playing metrics. The code below shows the details of this function and how it accounts for the media playing sequence.
Media playing sequence
Prerequisite: The media has been started (Media start).
App calls
Metrics.mediaPlay()to inform the Platform when media playback should start.App calls
Metrics.mediaLoadStart()to mark the initial request for the media asset (data URI is called).Content is shown to user. App calls
Metrics.MediaPlaying()to mark when content is playing.
/*
...Prerequisite: The media has been started (Media start)....
*/
function playById (id) {
if (hdcpSupport === false) {
Metrics.error(Metrics.ErrorType.MEDIA, 'CONTENT-004', 'HDCP not supported, video playback cancelled', true, { entityId: id })
return
}
const vid = videos.find(p => p.id === id)
if (vid) {
stop()
currentlyLoaded = vid
hls = new Hls()
hls.attachMedia(video)
// 1. App calls Metrics.mediaPlay() to inform the Platform when media playback should start.
Metrics.mediaPlay(id)
// 2. App calls mediaLoadStart() to mark the initial request for the media asset (data URI is called).
Metrics.mediaLoadStart(id)
hls.loadSource(vid.src)
// Autoplay after manifest is parsed
hls.on(Hls.Events.MANIFEST_PARSED, () => {
video.play()
// 3. Content is shown to user. App calls Metrics.MediaPlaying() (in this case automatically via event listener) to mark when content is playing.
})
} else {
Metrics.error(Metrics.ErrorType.MEDIA, 'CONTENT-001', 'We\'re sorry, that content is unavailable.' + id, true, { entityId: id })
}
}Media pause
Required Metrics APIs: Metrics.mediaPlaying(), Metrics.mediaPause(), Metrics.mediaPlay()
When the user pauses media during playback , Metrics.mediaPause() is called.
There are two types of media pauses on our platform:
User-initiated pauses: The user explicitly interacts with the application to pause the media. This can include actions such as clicking a pause control or opening a settings menu.
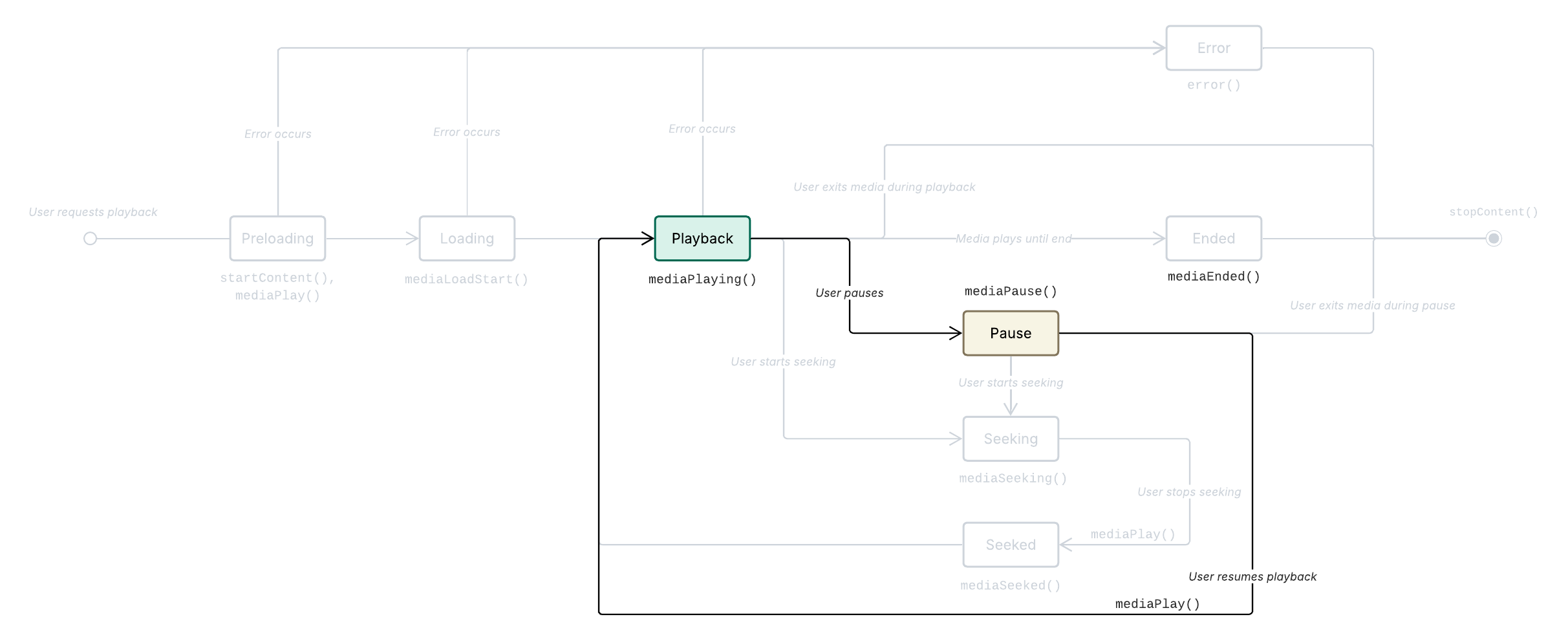
Platform-initiated pauses: The platform or application itself decides to pause the media based on certain conditions or events. This can include displaying an overlay advertisement or other business logic interruptions.
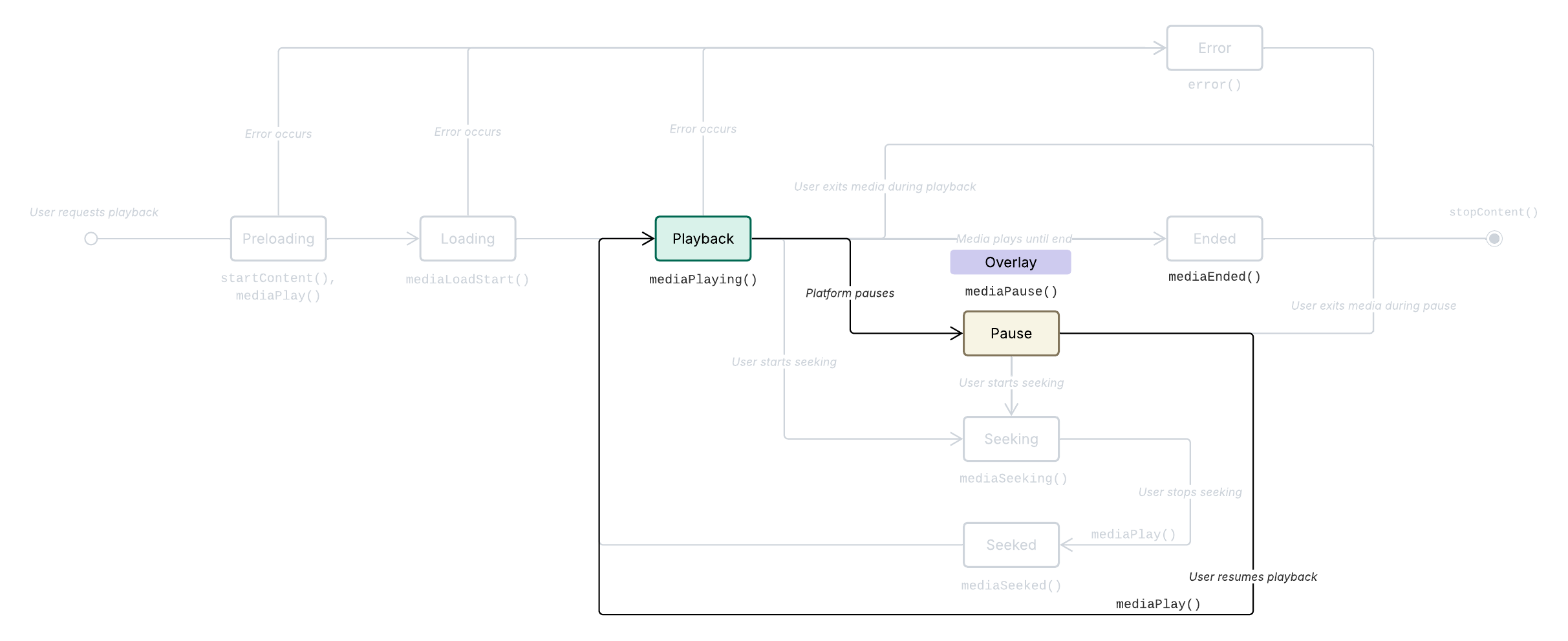
Media pause sequence
Prerequisite: The media has been started (Media start).
The user or platform pauses the content.
App calls
Metrics.mediaPause().
/*
...Prerequisite: The media has been started (Media start)...
*/
// 1. The user or platform pauses the content (represented here via Firebolt 'pause' intent).
if (intent.action == 'pause') {
const entityId = intent.data.entityId
// 2. App calls Metrics.mediaPause() (in this case, automatically via pause listener).
pause()
}Do not mark dynamic ad insertion as paused
Dynamic ad insertion into an ongoing playback of content should not be marked by a
Metrics.mediaPause()event since dynamic ad insertion is considered continuous playback. During the playback of ads, all playback events that can occur during the playback of regular content may be triggered if the business logic permits.
Media seeking and seeked
Required Metrics APIs: Metrics.mediaPlaying(), Metrics.mediaSeeking(), Metrics.mediaSeeked(), Metrics.mediaPlay()
When the user fast forwards, rewinds, or otherwise seeks through the loaded content, Metrics.mediaSeeking() and Metrics.mediaSeeked() are called.
Content seeking can be implemented in various ways within apps, such as having users:
Drag a slider to scrub through the content.
Click a ten-second jump button to jump forward or backwards in the content.
There are two general types of seeking interactions on our platform:
Seeking from playback: The user enters the seeking state during playback of media.
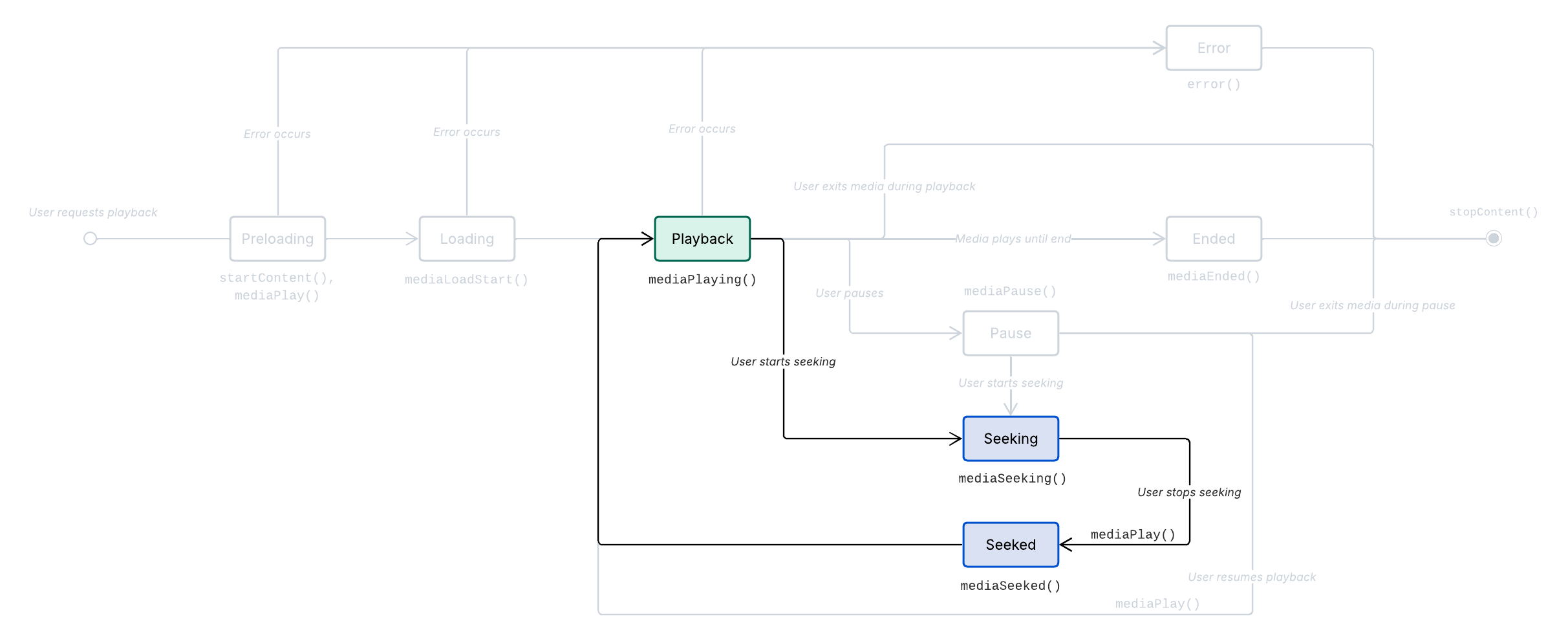
Seeking from pause: The user enters the seeking state while the media is paused.
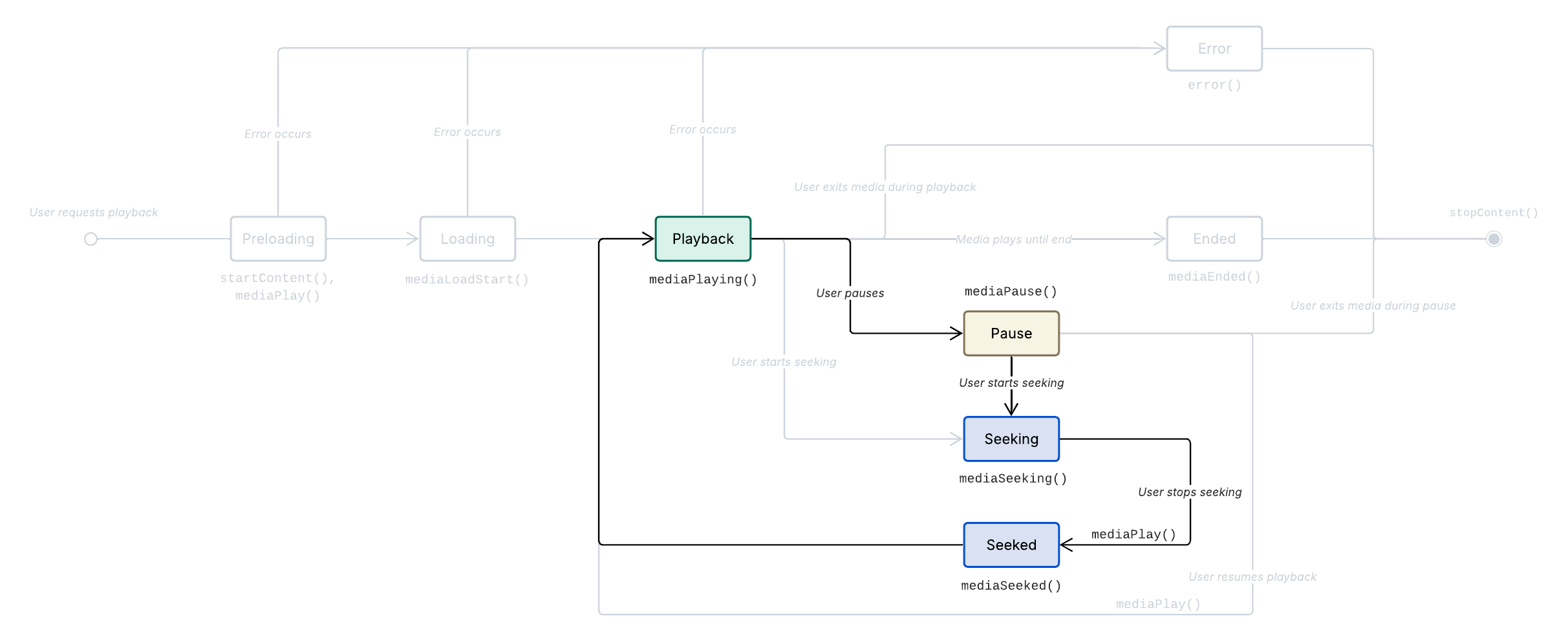
Media seeking and seeked sequence
Prerequisite: The media is playing (Media playing) OR The media is paused (Media pause).
User begins seeking through content.
Metrics.mediaSeeking()is called to mark intent to seek.User stops seeking through content.
Metrics.mediaPlay()is called to note that playback should begin again.Metrics.mediaSeeked()is called to mark end of seeking.Metrics.mediaPlaying()is called to mark the actual playback start.Media playback resumes in newly seeked position.
For this sequence, our seeking and seeked listeners will automatically listen for these events from elsewhere in our app and send the relevant metrics calls. Functionality for seeking and seeked state can be built according to your specific app’s needs.
/*
...Prerequisite: The media is playing (Media playing) OR The media is paused (Media pause)...
*/
function registerVideoEventListenersForMetrics (video) {
/*
...Additional listeners...
*/
// Log metrics for when seeking starts
video.addEventListener('seeking', () => {
Metrics.mediaSeeking(currentlyLoaded.id, progress())
})
// Log metrics for when seeking ends
video.addEventListener('seeked', () => {
Metrics.mediaSeeked(currentlyLoaded.id, progress())
})
}Handling successive seeking interactions
If the user performs quick successive seeking interactions, it is possible for several
Metrics.mediaSeeking()events to be triggered without all of them resulting in aMetrics.mediaSeeked()event. To account for this, your app can abort the processing of individualMetrics.mediaSeeking()events to consolidate them.
Media stopped
Required Metrics API: Metrics.stopContent()
When the user exits the loaded content before it has been played fully to the end, Metrics.stopContent() is called.
There are two general types of media stoppage on our platform:
Stop from playing: The user exits the media during the playback state.
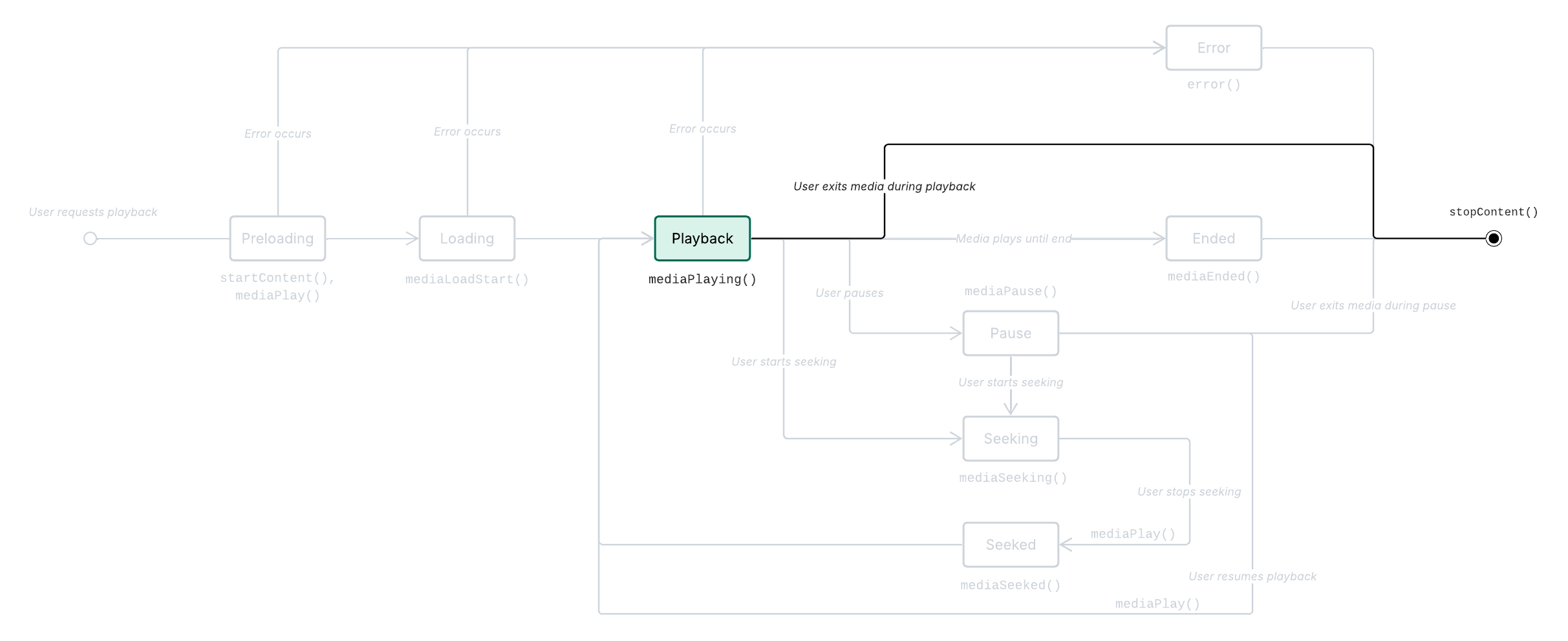
Stop from paused: The user exits the media during the paused state.
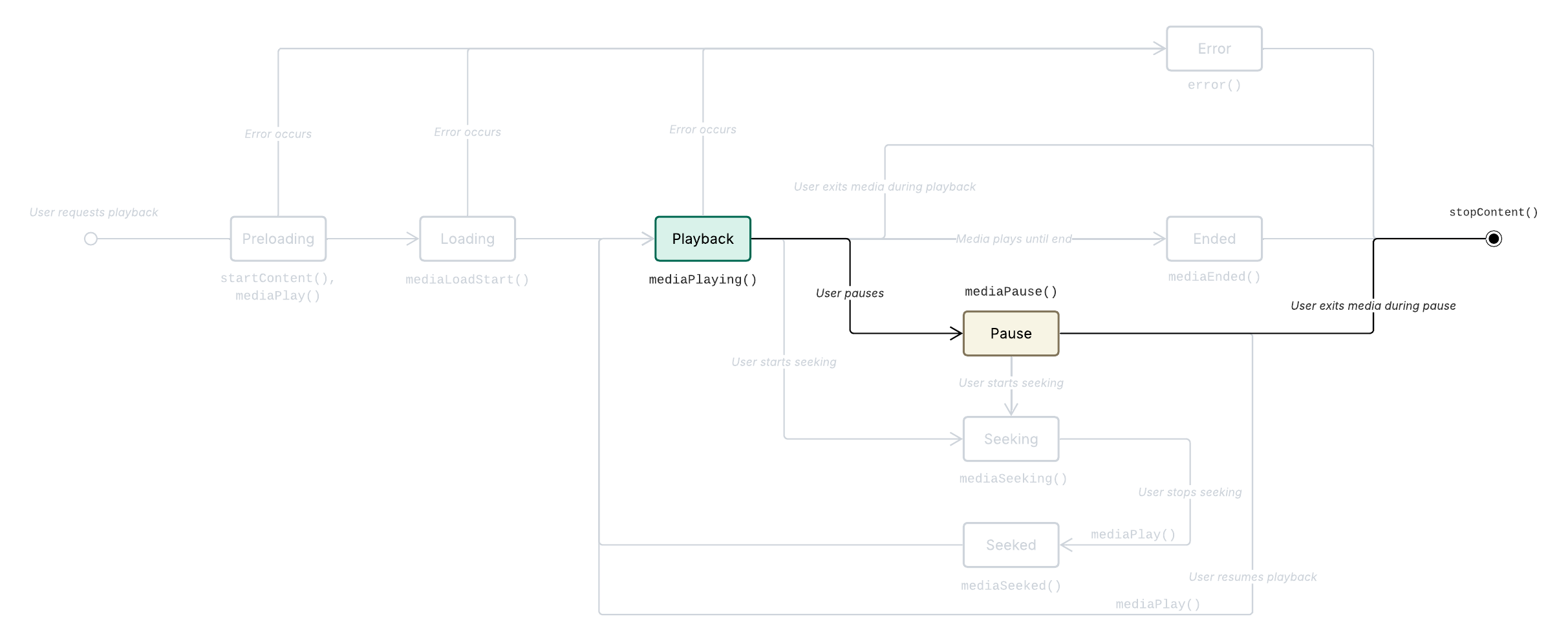
Media stopped sequence
Prerequisite: The media is playing (Media playing) OR The media is paused (Media pause).
The user exits the content.
App calls
Metrics.stopContent().
/*
...Prerequisite: The media is playing (Media playing) OR The media is paused (Media pause)...
*/
// 1. The user exits the content (represented here via the Firebolt 'home' intent).
if (intent.action == 'home') {
const entityId = intent.data.entityId
// 2. App calls Metrics.stopContent() (in this case, within stop() custom function).
stop()
}function stop () {
if (!isVideoLoaded()) return
if (currentlyLoaded != null) {
// 2. App calls Metrics.stopContent()
Metrics.stopContent(currentlyLoaded.id)
}
seekStop()
if (hls) {
hls.destroy()
}
hls = null
hidePlayerControls()
}Media ended
Required Metrics APIs: Metrics.mediaEnded(), Metrics.stopContent()
Metrics.mediaEnded() is called when the associated media reaches its conclusion after playback (including post-roll content if available). Like in the Media seeking and seeked scenario above, this sequence is handled automatically via the listeners we have set up previously.
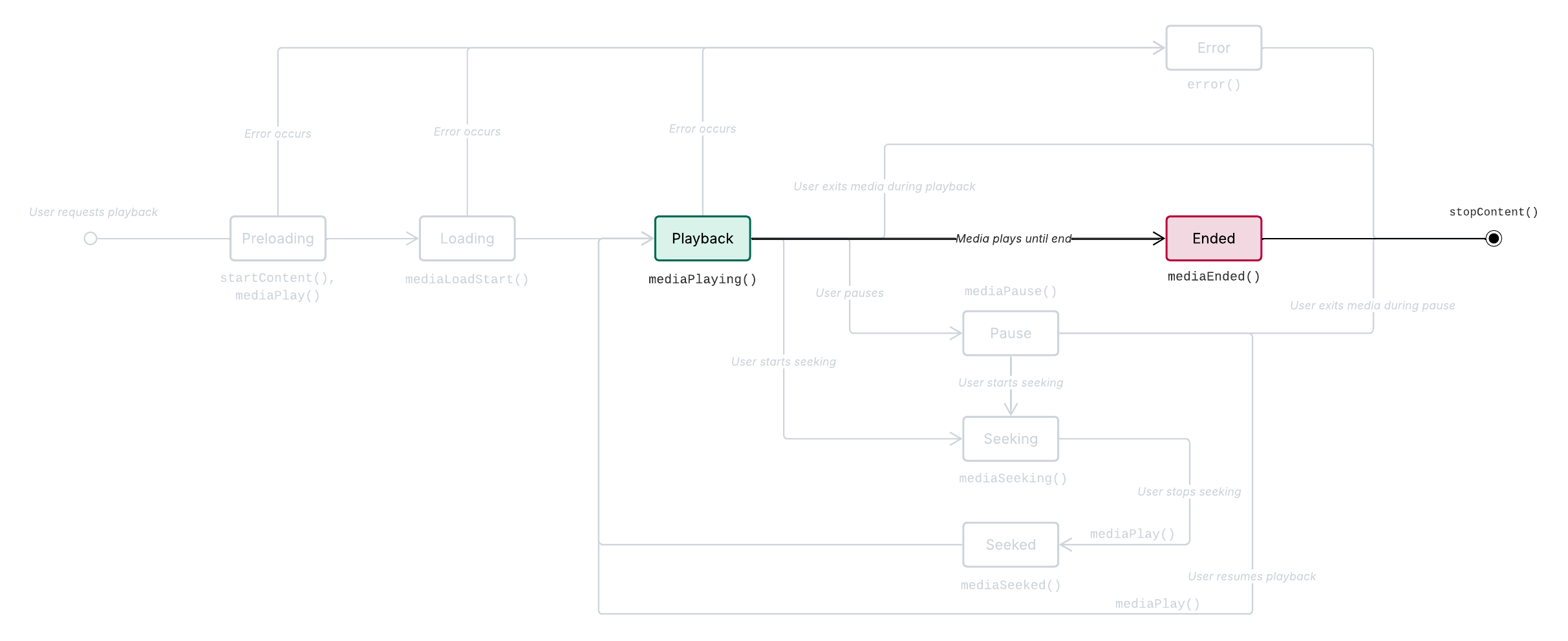
Media ended sequence
Prerequisite: The media is playing (Media playing).
User plays media asset until the end.
Metrics.mediaEnded()is called.User leaves content.
Metrics.stopContent()is called.
/*
...Prerequisite: The media is playing (Media playing)...
*/
function registerVideoEventListenersForMetrics (video) {
/*
...Additional listeners...
*/
// Once the video has ended, log a metric and hide the player controls
video.addEventListener('ended', () => {
Metrics.mediaEnded(currentlyLoaded.id)
// stop() function containing Metrics.stopContent() call
stop()
})
/*
...Additional Listeners...
*/
}Media rendition changed
Required Metrics API: Metrics.mediaRenditionChange()
A rendition change refers to the adjustment of the playback quality (either higher or lower) and involves changes in resolution and bitrate. This process is a key aspect of adaptive bitrate streaming, which ensures a smooth and uninterrupted viewing experience by dynamically adjusting the media quality based on network conditions and device capabilities.
Media rendition changes can be triggered due to:
Network bandwidth fluctuations: Changes in available network bandwidth can prompt a switch to a higher or lower bitrate to maintain smooth playback.
Device performance: Variations in device CPU or GPU performance can necessitate adjustments in resolution and bitrate to ensure optimal playback quality.
Buffering events: Occurrences of buffering due to network congestion or other interruptions can trigger a downgrade in quality to prevent playback stalling.
Relevant user actions: User interactions such as switching to full-screen mode or changing playback settings can lead to a rendition change to match the new display requirements.
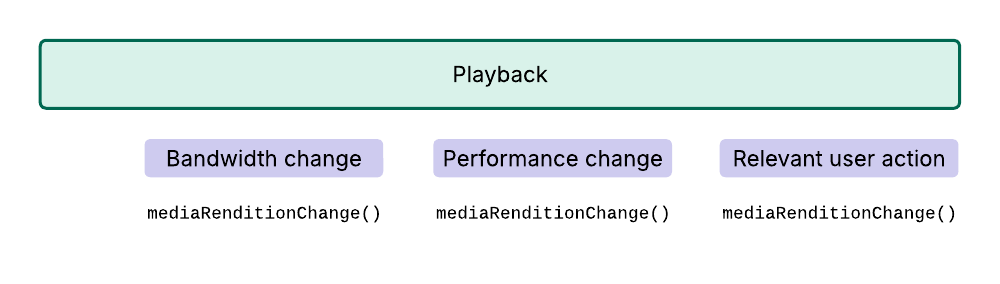
Media rendition changed sequence
Prerequisite: The media is playing (Media playing).
The bitrate or resolution of the media is changed.
Metrics.mediaRenditionChange()is called.
/*
...Prerequisite: The media is playing (Media playing)...
*/
// Detect rendition changes to send as metrics
// 1. The bitrate or resolution of the media is changed.
hls.on(Hls.Events.LEVEL_SWITCHED, (event, data) => {
const levelInfo = hls.levels[data.level]
// 2. Metrics.mediaRenditionChange() is called.
Metrics.mediaRenditionChange(currentlyLoaded.id, levelInfo.bitrate, levelInfo.width, levelInfo.height, levelInfo.codecSet)
})Error metrics
Media start preloading error
Required Metrics APIs: Metrics.startContent(), Metrics.mediaPlay(), Metrics.error(), Metrics.stopContent()
Errors can occur during the preloading phase of an asset, which is when the asset has been requested by the user, and the Metrics.startContent() and Metrics.mediaPlay() APIs have already been called. Since the error is unrecoverable, the loading process does not start. This typically results in an error message being displayed to the user.
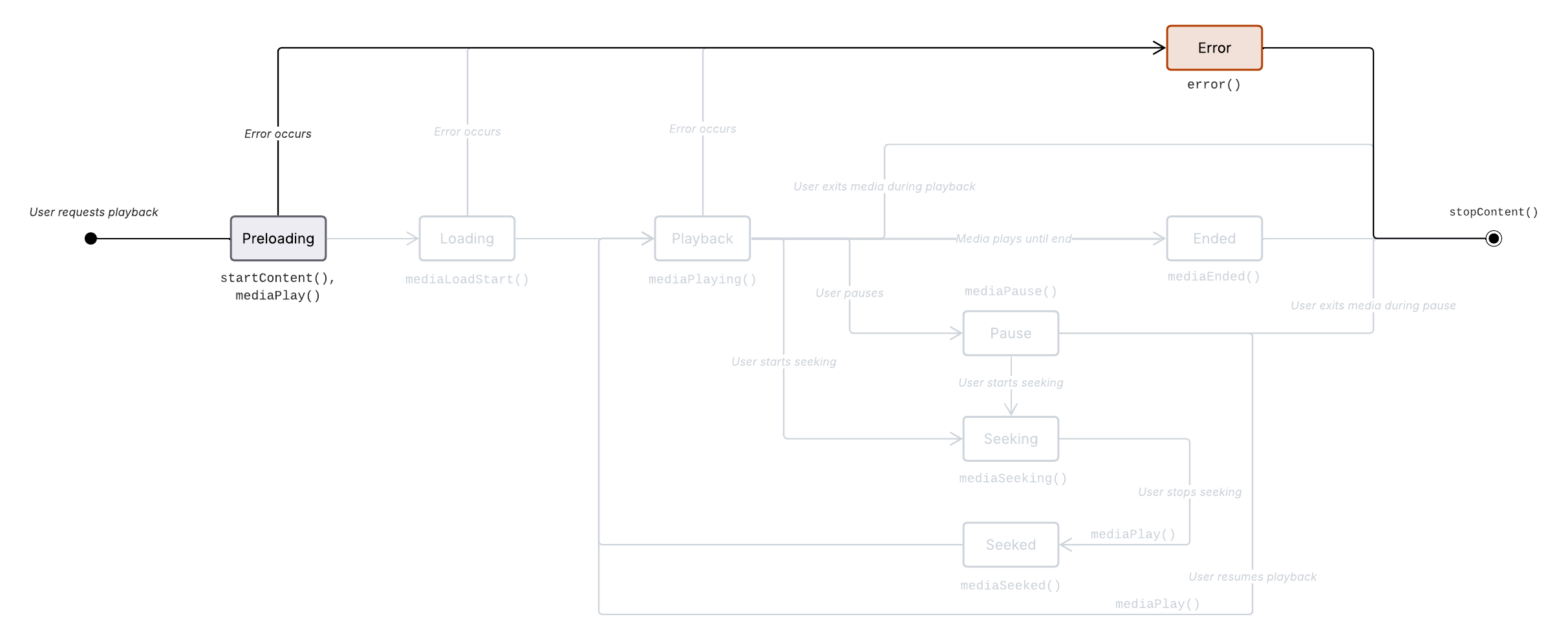
Media start preloading error sequence
Prerequisite: The media has been started (Media start).
App calls
Metrics.mediaPlay()to inform the Platform when media playback should start.Non-recoverable error occurs.
Metrics.error()called.User or app requests to leave content.
Metrics.stopContent()called.
/*
...Prerequisite: The media has been started (Media start)...
*/
function playById (id) {
if (hdcpSupport === false) {
Metrics.error(Metrics.ErrorType.MEDIA, 'CONTENT-004', 'HDCP not supported, video playback cancelled', true, { entityId: id })
return
}
const vid = videos.find(p => p.id === id)
if (vid) {
stop()
currentlyLoaded = vid
hls = new Hls()
hls.attachMedia(video)
// 1. App calls Metrics.mediaPlay() to inform the Platform when media playback should start.
Metrics.mediaPlay(id)
Metrics.mediaLoadStart(id)
hls.loadSource(vid.src)
// Autoplay after manifest is parsed
hls.on(Hls.Events.MANIFEST_PARSED, () => {
video.play()
})
} else {
// 2. Non-recoverable error occurs. Metrics.error() called.
Metrics.error(Metrics.ErrorType.MEDIA, 'CONTENT-001', 'We\'re sorry, that content is unavailable.' + id, true, { entityId: id })
// 3. User or app requests to leave content. Error listener automatically calls stop() function with Metrics.stopContent()
}
}Media start loading error
Required Metrics APIs: Metrics.startContent(), Metrics.mediaPlay(), Metrics.mediaLoadStart(), Metrics.error(), Metrics.stopContent()
Errors can occur during the loading phase of an asset. This phase begins with the request for the asset URI (i.e., manifest file) accompanied by the Metrics.mediaLoadStart() call.
Common errors at the loading stage include:
The manifest file being unavailable or in an incorrect format.
The content itself being unavailable on the CDN.
A poor network connection causing a timeout.
These errors are unrecoverable and typically result in an error message being displayed to the user.
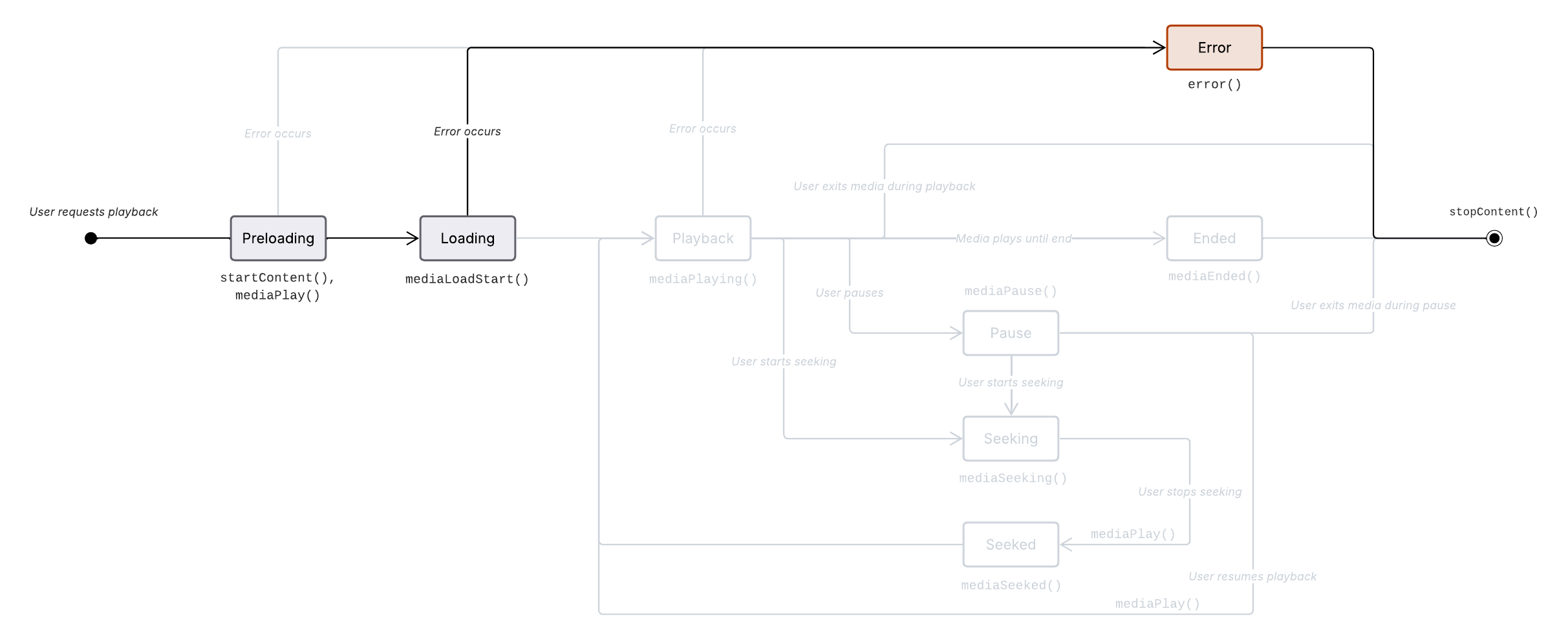
Media start loading error sequence
Prerequisite: The media has been started (Media start).
App calls
Metrics.mediaPlay()to inform the Platform when media playback should start.Initial request for the media asset is made (Data URI is called) via
Metrics.mediaLoadStart().Non-recoverable error occurs.
Metrics.error()called.User or app requests to leave content.
Metrics.stopContent()called.
/*
...Prerequisite: The media has been started (Media start)...
*/
function playById (id) {
if (hdcpSupport === false) {
Metrics.error(Metrics.ErrorType.MEDIA, 'CONTENT-004', 'HDCP not supported, video playback cancelled', true, { entityId: id })
return
}
const vid = videos.find(p => p.id === id)
if (vid) {
stop()
currentlyLoaded = vid
hls = new Hls()
hls.attachMedia(video)
// 1. App calls metrics.mediaPlay() to inform the Platform when media playback should start.
Metrics.mediaPlay(id)
// 2. Initial request for the media asset is made (Data URI is called) via mediaLoadStart().
Metrics.mediaLoadStart(id)
hls.loadSource(vid.src)
// Autoplay after manifest is parsed
hls.on(Hls.Events.MANIFEST_PARSED, () => {
video.play()
// video.addEventListener() automatically calls Metrics.mediaPlaying() as a result of the change.
})
} else {
// 3. Non-recoverable error occurs. Metrics.error() called
Metrics.error(Metrics.ErrorType.MEDIA, 'CONTENT-001', 'We\'re sorry, that content is unavailable.' + id, true, { entityId: id })
// 4. User or app requests to leave content. Error listener automatically calls stop() function with Metrics.stopContent()
}
}Media playing error
Required Metrics APIs: Metrics.startContent(), Metrics.mediaPlay(), Metrics.mediaLoadStart(), Metrics.mediaPlaying(), Metrics.error(), Metrics.stopContent()
A media playing error refers to instances where media playback is interrupted or fails to continue smoothly after it has started. This type of error can be triggered by problems with the video data itself, such as corruption or encoding errors.
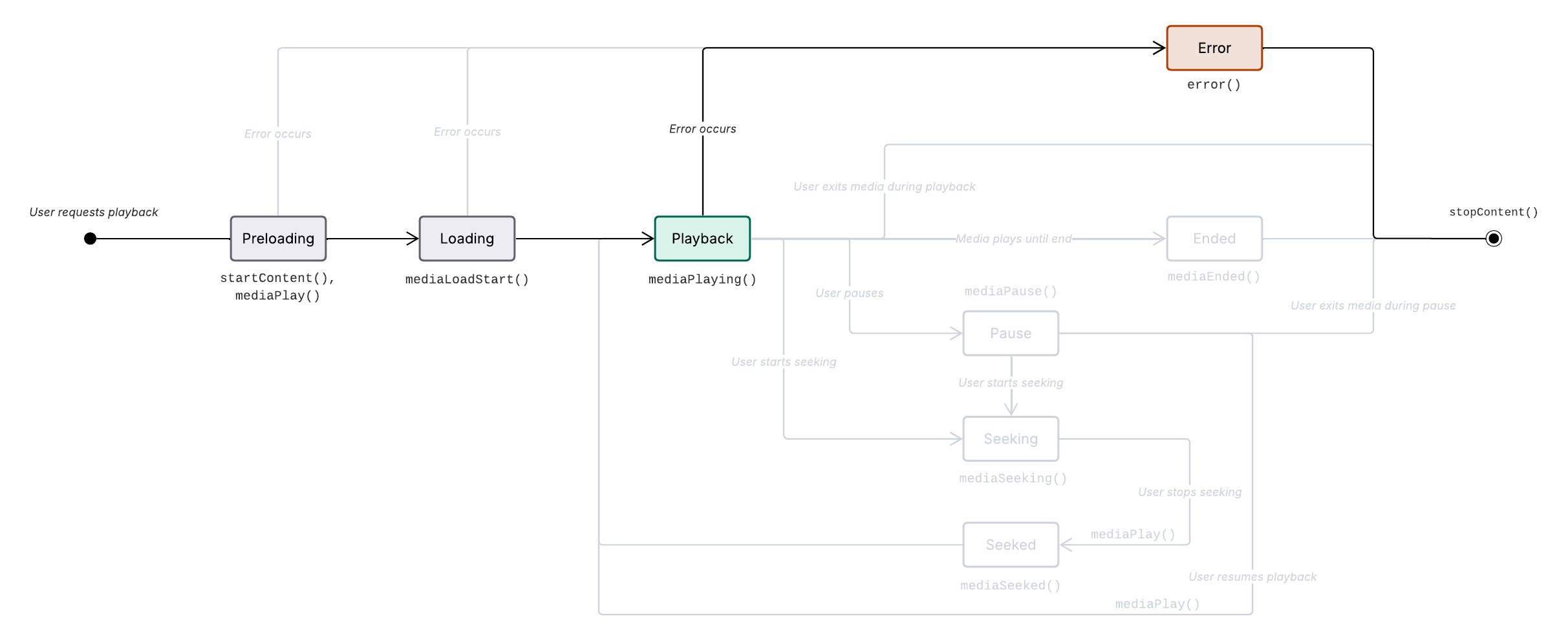
Media playing error sequence
Prerequisite: The media is playing (Media playing).
Non-recoverable error occurs.
Metrics.error()called.User or app requests to leave content.
Metrics.stopContent()called.
function playById (id) {
if (hdcpSupport === false) {
Metrics.error(Metrics.ErrorType.MEDIA, 'CONTENT-004', 'HDCP not supported, video playback cancelled', true, { entityId: id })
return
}
const vid = videos.find(p => p.id === id)
if (vid) {
/*
...Prerequisite: The media is playing (Media playing)...
*/
} else {
// 1. Non-recoverable error occurs. Metrics.error() called.
Metrics.error(Metrics.ErrorType.MEDIA, 'CONTENT-001', 'We\'re sorry, that content is unavailable.' + id, true, { entityId: id })
// 2. User or app requests to leave content. Error listener automatically calls stop() function with Metrics.stopContent()
}
}